Appearance
仿射变换
引言
什么是仿射变换
仿射变换简单的讲就是线性变换和平移 。在线性变换中,每个向量都会按照相同的比例被缩放,也就是说,它们之间的线性关系在变换后保持不变。这种变换可以应用于多种领域,例如计算机图形学、物理学、经济学等等。在计算机图形学中,线性变换常用于描述平移、旋转、缩放等操作。
请牢记最后这句话。
为什么要学习仿射变换
学习仿射变换的原因很多,其中最重要的原因是因为仿射变换可以用来描述和改变图像和物体在二维或三维空间中的位置、形状和方向等特征,对于计算机图形学和计算机视觉领域的应用非常广泛。例如,在游戏和动画中,我们可以使用仿射变换来制作出各种不同的视觉效果,比如旋转、平移、缩放和扭曲等。
说人话就是:如果不学习仿射变换,我们将不能控制物体在我们的场景中进行移动!
本文将要介绍的内容
首先,我们已经介绍了什么是仿射变换以及为什么我们要学习仿射变换。接下来将从以下几部分展开。
- 仿射变换涉及到基本的数学知识,比如向量与矩阵的运算。所以我们会简要的介绍一下关于这部分的知识。我们将使用向量与矩阵来表示我们的仿射变换过程。
- 接着,我们将介绍仿射变换的基本类型,包括平移、旋转、缩放类型。
- 然后,我们将探索一下多个仿射变换在不同组合的情况下会发生什么事情。
- 最后,我们将通过实际案例和实例代码俩演示如何在实践中应用仿射变换。
坐标系与向量
笛卡尔坐标系
笛卡尔坐标系是由法国哲学家、数学家笛卡尔(René Descartes)发明的一种用于描述平面和空间中点位置的坐标系统。它是一种直角坐标系,包含了两条互相垂直的坐标轴,通常用 x 和 y 来表示平面坐标系,用 x、y 和 z 来表示空间坐标系。
在笛卡尔坐标系中,每个点都可以由一组坐标来表示。对于二维平面坐标系而言,一个点的坐标通常被表示为 (x, y) 的形式,其中 x 表示该点在 x 轴上的位置,y 表示该点在 y 轴上的位置。对于三维空间坐标系而言,则需要用三个坐标 (x, y, z) 来表示。
想必这一部分的知识各位读者应该都很清楚了吧~
向量的定义及运算
向量是有大小和方向的量,通常用箭头来表示。向量可以在二维或三维空间中表示,每个向量都有一个起点和一个终点。向量的长度被称为模,可以用数值表示。向量的方向可以用角度或者用一个具有方向的单位向量来表示。
如下图所示,用代数的方式表示一个向量,可以将其写作:
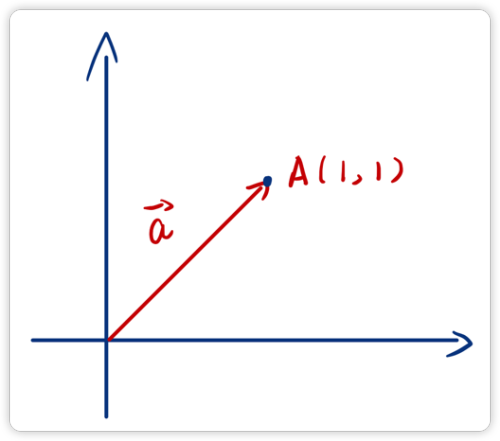
但是,我们需要注意的是一个点的坐标表示与向量的表示在形式上是一样的,比如向量 与点 的表示形式都是 但是他们表示的含义是截然不同的。
向量 表示的是一个从原点为起点,指向 位置的具有方向和长度的量,而点 仅仅只是表示坐标系中的一个位置。这一点需要大家分清!
向量的基本运算法则
假设现在我们有两个向量 与 。
- 加法:,减法同理。
- 点乘:点乘是向量运算的一种,也被称为内积或数量积。点乘有许多应用,例如计算两个向量之间的夹角、计算向量的长度等等。在计算机图形学中,点乘还被广泛应用于计算光照效果、投影等方面。其运算规则如下:
关于点乘需要注意的是,两个向量他们的点乘结果不再是向量,而是一个标量了。
- 叉乘是向量运算中的一种,通常表示为 ,结果是另一个向量。它的运算规则是: 的结果是垂直于 和 的向量,方向由右手定则确定,大小为 ,其中 是 和 之间的夹角。因此,叉乘的结果是一个与 和 都垂直的向量,其大小等于两个向量张成的平行四边形的面积。
矩阵表示
如下所示,矩阵是一个由数值排列成的矩形阵列,通常用方括号括起来表示。我们可以简单将其理解为是一种特殊的排列数字的方式,它有着属于自己的一套运算规则,仅此而已。
本文的向量与矩阵表示约定
我们本文中所说的向量与矩阵都使用粗体来进行表示:
向量 与 矩阵
一般指的都是列向量,表示为:
但是由于列向量在页面排版上比较占据空间,所以我们使用转置符号和行向量来表示列向量。
以上两种表示向量的方式等价。
矩阵的乘法运算法则
在计算机图形学中,我们经常会遇到的数学问题就是向量与矩阵进行乘法操作。那么我们需要理解矩阵是如何进行乘法运算的。
首先,我们需要明白一点就是不是所有的矩阵和矩阵之间都能够进行乘法操作。假设我们有两个矩阵 与 这两个矩阵必须要满足 时,他们才可以进行乘法操作。
我们可以将向量作一种特殊的矩阵,比如向量 我们可以将其看做是一个 的矩阵。那么一个 的矩阵与其相乘后,我们同样也会得到一个 的矩阵。也就是一个向量了。
下面给出矩阵与矩阵的乘法表示:
矩阵与矩阵之间相乘
也可以抽象的表示为:
基本变换
线性变换的矩阵表示
缩放
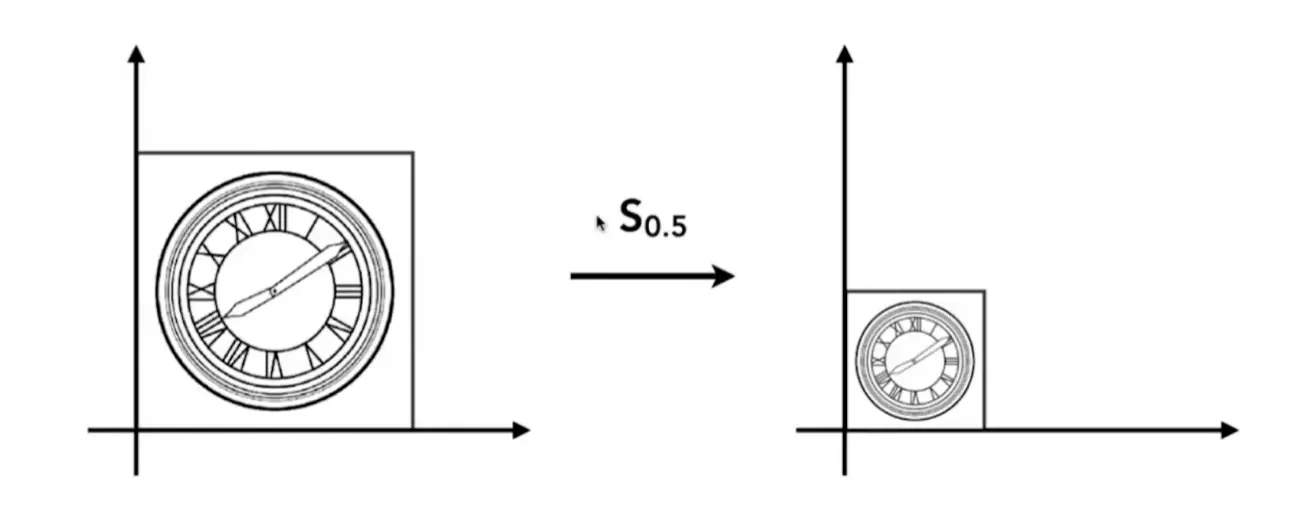 缩放是最容易理解的一种线性变换,就是简单给 x, y 分别乘上一个值即可。用代数表示可以写为:
缩放是最容易理解的一种线性变换,就是简单给 x, y 分别乘上一个值即可。用代数表示可以写为:
根据矩阵的乘法规则,我们可以将其改写为:
旋转
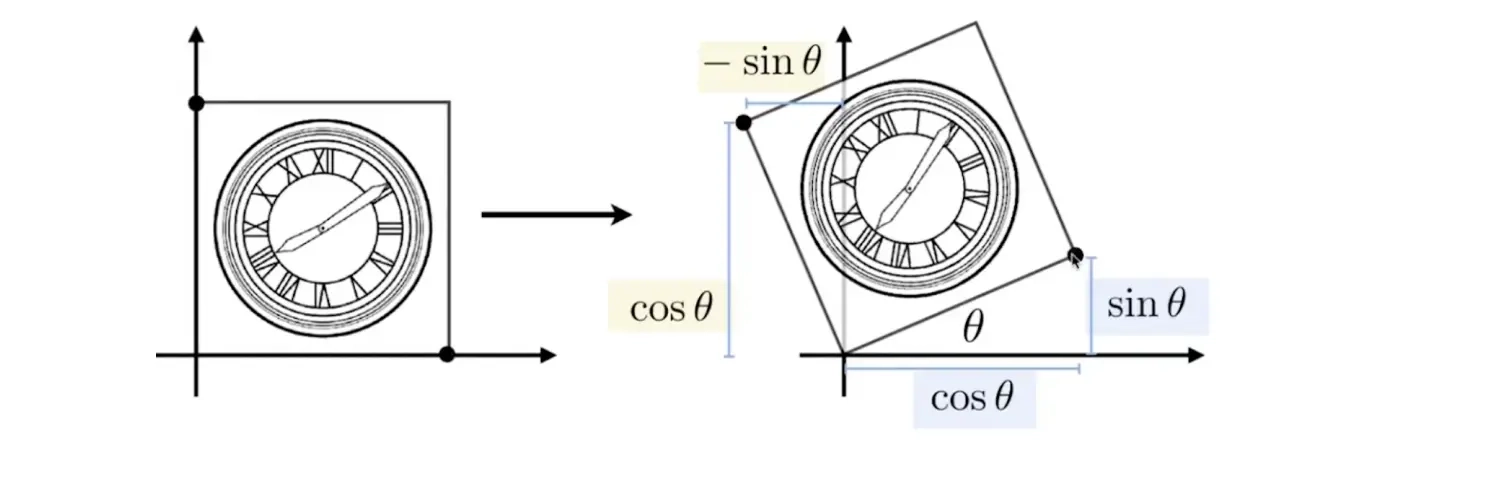
旋转就稍微的要复杂一点了,我们先给出旋转的代数表达式和矩阵表示
为什么是这样,下图有详细的推导过程: 
仿射变换的矩阵表示
平移
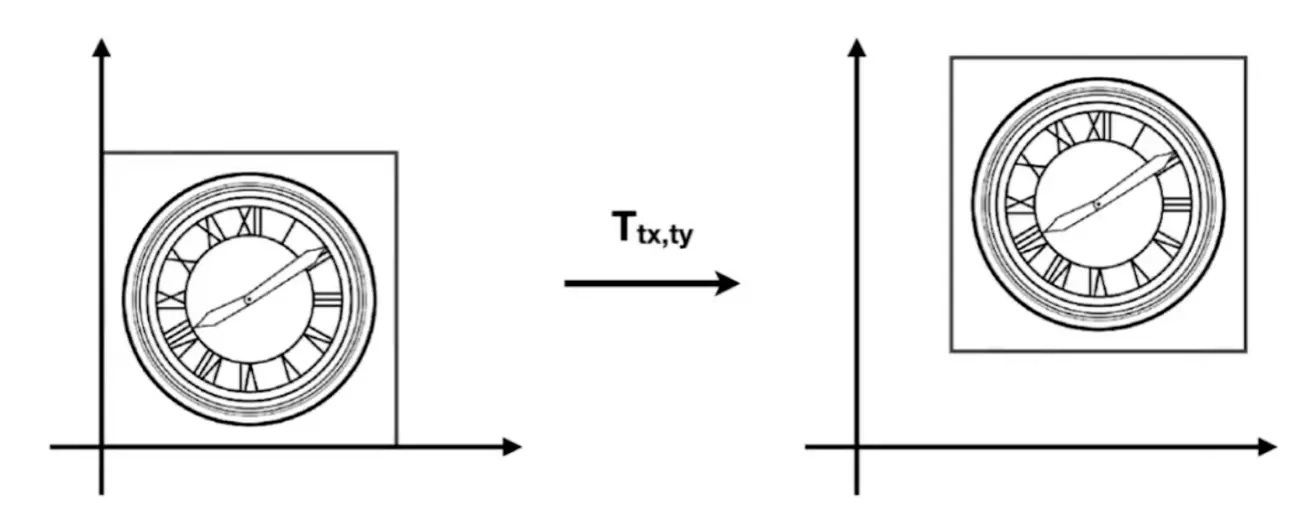
平移的表示就更加的简单了,就是给坐标加上一个数就是表示平移。我们发现,对于二维坐标,我们无法使用 2x2 的矩阵和 2 维向量的乘法来表示这样的加减关系(如下列公式所示)。
为了解决平移在矩阵中的表示问题,齐次坐标应运而生了。
齐次坐标
平面上的任何点都可以表示成一三元组 (X, Y, W),称之为该点的齐次坐标
当 W 不为 0,则该点表示欧氏平面上的 (X/W, Y/W)
那么,我们使用齐次坐标表示平移,如下:
同理的,对于缩放和旋转我们也可以改写为
复合变换
复杂的事情现在来了,如果我们将平移、旋转、缩放这三种变换组合起来会发生什么样的奇妙反应呢?读者可以先在下方的 demo 中尝试一下调整平移、缩放和旋转属性,我们可以发现虽然平移、旋转、缩放这三者的值是一样的。但是由于他们的组合顺序不同,我们最终看到的结果也是截然不同的。所以变换组合的顺序也是至关重要的!
TranslateX:
TranslateY:
Rotate:
Scale:
translate(50, 75),rotate(55.0), scale(1.0)

scale(1.0), rotate(55.0), translate(50, 75)

应用实例
现在我们将其应用到我们的 WebGL 程序中。我依然使用我们在上一章中使用的代码,不过为了应用我们的仿射变换,我们需要额外的引入一些 uniform 变量。分别为:u_translate, u_rotate, u_scale,它们分别表示平移、旋转、缩放矩阵。 我们需要修改我们的顶点着色器
js
// 顶点着色器
const vertexShader = `
attribute vec4 a_position;
uniform mat4 u_translate;
uniform mat4 u_rotate;
uniform mat4 u_scale;
void main () {
// gl_Position = a_position;
gl_Position = u_translate * u_rotate * u_scale * a_position;
}
`;我们现在已经在我们 shader 中声明了我们的矩阵,现在我们需要在 js 中获取 shader 中的变量,并且“赋值”给它。这里的“赋值”为什么打了引号,因为它并不是等价于我们 js 中的赋值。不过这里我暂且就这样理解。
我们还额外的引入了gl-matrix的库来帮助我们快速的生成平移、旋转、缩放矩阵。我
js
let translateX = 0;
let translateY = 0;
let rotateRadian = 0;
let scale = 1;
const translateMat = mat4.create();
const rotateMat = mat4.create();
const scaleMat = mat4.create();
mat4.translate(translateMat, translateMat, [translateX, translateY, 0]);
mat4.rotate(rotateMat, rotateMat, rotateRadian, [0, 0, 1]);
mat4.scale(scaleMat, scaleMat, [scale, scale, scale]); 现在我们要将我们生成的矩阵传入到我们的 Shader 中,首先我们需要通过 gl.getUniformLocation 这个 API 获取我们 Shader 中 uniform 变量的位置,然后再利用 gl.uniformMatrix4fv API 将我们的矩阵传入到 Shader 中,代码如下:
js
// 我们需要往shader中传入矩阵
const uTranslateLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_translate');
const uRotateLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_rotate');
const uScaleLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_scale');
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uTranslateLoc, false, translateMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uRotateLoc, false, rotateMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uScaleLoc, false, scaleMat); 完整的代码及 demo 如下:
ts
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl');
if (!gl) {
return null;
}
// 设置清空颜色缓冲区时的颜色
gl.clearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// 清空颜色缓冲区
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// 顶点着色器
const vertexShader = `
attribute vec4 a_position;
uniform mat4 u_translate;
uniform mat4 u_rotate;
uniform mat4 u_scale;
void main () {
// gl_Position = a_position;
gl_Position = u_translate * u_rotate * u_scale * a_position;
}
`;
// 片元着色器
const fragmentShader = `
// 设置浮点数精度
precision mediump float;
void main () {
// vec4是表示四维向量,这里用来表示RGBA的值[0~1],均为浮点数,如为整数则会报错
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// 初始化shader程序
const program = initWebGL(gl, vertexShader, fragmentShader);
if (!program) {
return null;
}
// 告诉WebGL使用我们刚刚初始化的这个程序
gl.useProgram(program);
const pointPos = [-0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5];
const buffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
// -----------------------------------------------------
// 注意:这里必须采用类型化数组往WebGL传入attribute类型的数据
// -----------------------------------------------------
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(pointPos), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// 获取shader中a_position的地址
const a_position = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_position');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
// gl.vertexAttrib3f(a_position, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// 采用vertexAttribPointer进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_position,
2,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 2,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_position);
// 我们需要往shader中传入矩阵
const uTranslateLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_translate');
const uRotateLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_rotate');
const uScaleLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_scale');
let translateX = 0;
let translateY = 0;
let rotateRadian = 0;
let scale = 1;
const render = () => {
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
const translateMat = mat4.create();
const rotateMat = mat4.create();
const scaleMat = mat4.create();
mat4.translate(translateMat, translateMat, [translateX, translateY, 0]);
mat4.rotate(rotateMat, rotateMat, rotateRadian, [0, 0, 1]);
mat4.scale(scaleMat, scaleMat, [scale, scale, scale]);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uTranslateLoc, false, translateMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uRotateLoc, false, rotateMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uScaleLoc, false, scaleMat);
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
};
render();ts
import { mat4, vec3 } from 'gl-matrix';
import { Camera, Matrix4, Object3D, PerspectiveCamera, Vector3 } from 'three';
function createShader(gl: WebGLRenderingContext, type: number, source: string) {
// 创建 shader 对象
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
// 往 shader 中传入源代码
gl.shaderSource(shader!, source);
// 编译 shader
gl.compileShader(shader!);
// 判断 shader 是否编译成功
const success = gl.getShaderParameter(shader!, gl.COMPILE_STATUS);
if (success) {
return shader;
}
// 如果编译失败,则打印错误信息
console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader!));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
}
function createProgram(
gl: WebGLRenderingContext,
vertexShader: WebGLShader,
fragmentShader: WebGLShader
): WebGLProgram | null {
// 创建 program 对象
const program = gl.createProgram();
// 往 program 对象中传入 WebGLShader 对象
gl.attachShader(program!, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(program!, fragmentShader);
// 链接 program
gl.linkProgram(program!);
// 判断 program 是否链接成功
const success = gl.getProgramParameter(program!, gl.LINK_STATUS);
if (success) {
return program;
}
// 如果 program 链接失败,则打印错误信息
console.log(gl.getProgramInfoLog(program!));
gl.deleteProgram(program);
return null;
}
export function initWebGL(
gl: RenderContext,
vertexSource: string,
fragmentSource: string
) {
// 根据源代码创建顶点着色器
const vertexShader = createShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vertexSource);
// 根据源代码创建片元着色器
const fragmentShader = createShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentSource);
// 创建 WebGLProgram 程序
const program = createProgram(gl, vertexShader!, fragmentShader!);
return program;
}
export enum REPEAT_MODE {
NONE,
REPEAT,
MIRRORED_REPEAT,
}
export function createTexture(gl: WebGLRenderingContext, repeat?: REPEAT_MODE) {
const texture = gl.createTexture();
gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, texture);
gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, gl.LINEAR);
gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, gl.LINEAR);
let mod: number = gl.CLAMP_TO_EDGE;
switch (repeat) {
case REPEAT_MODE.REPEAT:
mod = gl.REPEAT;
break;
case REPEAT_MODE.MIRRORED_REPEAT:
mod = gl.MIRRORED_REPEAT;
break;
}
gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_WRAP_S, mod);
gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_WRAP_T, mod);
return texture;
}
export function isMobile(): boolean {
if (typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.navigator) {
const userAgent = window.navigator.userAgent;
return /(mobile)/i.test(userAgent);
}
return false;
}
export function clamp(x: number, min: number, max: number) {
if (x < min) {
x = min;
} else if (x > max) {
x = max;
}
return x;
}
export function readLUTCube(file: string): {
size: number;
data: number[];
} {
let lineString = '';
let isStart = true;
let size = 0;
let i = 0;
let result: number[] = [];
const processToken = (token: string) => {
if (token === 'LUT size') {
i++;
let sizeStart = false;
let sizeStr = '';
while (file[i] !== '\n') {
if (file[i - 1] === ' ' && /\d/.test(file[i])) {
sizeStart = true;
sizeStr += file[i];
} else if (sizeStart) {
sizeStr += file[i];
}
i++;
}
size = +sizeStr;
result = new Array(size * size * size);
} else if (token === 'LUT data points') {
// 读取数据
i++;
let numStr = '';
let count = 0;
while (i < file.length) {
if (/\s|\n/.test(file[i])) {
result[count++] = +numStr;
numStr = '';
} else if (/\d|\./.test(file[i])) {
numStr += file[i];
}
i++;
}
}
};
for (; i < file.length; i++) {
if (file[i] === '#') {
isStart = true;
} else if (isStart && file[i] === '\n') {
processToken(lineString);
lineString = '';
isStart = false;
} else if (isStart) {
lineString += file[i];
}
}
return {
size,
data: result,
};
}
export async function loadImages(srcs: string[]): Promise<HTMLImageElement[]> {
const all: Promise<HTMLImageElement>[] = srcs.map(item => loadImage(item));
return Promise.all(all);
}
export async function loadImage(src: string) {
return new Promise<HTMLImageElement>(resolve => {
const img = new Image();
img.src = src;
img.onload = () => {
resolve(img);
};
});
}
export function compute8ssedt(image: ImageData): number[][] {
// Initialize distance transform image
const distImage: number[][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < image.height; i++) {
distImage[i] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < image.width; j++) {
distImage[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Initialize queue for distance transform
const queue: number[][] = [];
const data = image.data;
for (let i = 0; i < image.height; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < image.width; j++) {
const index = (i * image.width + j) * 4;
if (data[index] == 255) {
queue.push([i, j]);
}
}
}
// Compute distance transform
while (queue.length > 0) {
const p = queue.shift()!;
const x = p[0];
const y = p[1];
let minDist = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
let minDir = [-1, -1];
// Compute distance to nearest foreground pixel in 8 directions
for (let i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
for (let j = -1; j <= 1; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;
const nx = x + i;
const ny = y + j;
if (
nx >= 0 &&
nx < image.height &&
ny >= 0 &&
ny < image.width
) {
const d = distImage[nx][ny] + Math.sqrt(i * i + j * j);
if (d < minDist) {
minDist = d;
minDir = [i, j];
}
}
}
}
// Update distance transform image and queue
distImage[x][y] = minDist;
if (minDir[0] != -1 && minDir[1] != -1) {
const nx = x + minDir[0];
const ny = y + minDir[1];
if (distImage[nx][ny] == 0) {
queue.push([nx, ny]);
}
}
}
return distImage;
}
// #region createFramebuffer
export function createFramebufferAndTexture(
gl: WebGLRenderingContext,
width: number,
height: number
): [WebGLFramebuffer | null, WebGLTexture | null] {
const framebuffer = gl.createFramebuffer();
gl.bindFramebuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, framebuffer);
const texture = createTexture(gl, REPEAT_MODE.NONE);
gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, texture);
gl.texImage2D(
gl.TEXTURE_2D,
0,
gl.RGBA,
width,
height,
0,
gl.RGBA,
gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE,
null
);
gl.framebufferTexture2D(
gl.FRAMEBUFFER,
gl.COLOR_ATTACHMENT0,
gl.TEXTURE_2D,
texture,
0
);
const status = gl.checkFramebufferStatus(gl.FRAMEBUFFER);
if (status === gl.FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE) {
gl.bindFramebuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, null);
gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, null);
return [framebuffer, texture];
}
return [null, null];
}
// #endregion createFramebuffer
// #region lookat
export function lookAt(cameraPos: vec3, targetPos: vec3): mat4 {
const z = vec3.create();
const y = vec3.fromValues(0, 1, 0);
const x = vec3.create();
vec3.sub(z, cameraPos, targetPos);
vec3.normalize(z, z);
vec3.cross(x, y, z);
vec3.normalize(x, x);
vec3.cross(y, z, x);
vec3.normalize(y, y);
// prettier-ignore
return mat4.fromValues(
x[0], x[1], x[2], 0,
y[0], y[1], y[2], 0,
z[0], z[1], z[2], 0,
cameraPos[0], cameraPos[1], cameraPos[2], 1
);
}
// #endregion lookat
export function ASSERT(v: any) {
if (v === void 0 || v === null || isNaN(v)) {
throw new Error(v + 'is illegal value');
}
}
const lightAttenuationTable: Record<string, number[]> = {
'7': [1, 0.7, 1.8],
'13': [1, 0.35, 0.44],
'20': [1, 0.22, 0.2],
'32': [1, 0.14, 0.07],
'50': [1, 0.09, 0.032],
'65': [1, 0.07, 0.017],
'100': [1, 0.045, 0.0075],
'160': [1, 0.027, 0.0028],
'200': [1, 0.022, 0.0019],
'325': [1, 0.014, 0.0007],
'600': [1, 0.007, 0.0002],
'3250': [1, 0.0014, 0.000007],
};
// #region attenuation
export function lightAttenuationLookUp(dist: number): number[] {
const distKeys = Object.keys(lightAttenuationTable);
const first = +distKeys[0];
if (dist <= first) {
return lightAttenuationTable['7'];
}
for (let i = 0; i < distKeys.length - 1; i++) {
const key = distKeys[i];
const nextKey = distKeys[i + 1];
if (+key <= dist && dist < +nextKey) {
const value = lightAttenuationTable[key];
const nextValue = lightAttenuationTable[nextKey];
const k = (dist - +key) / (+nextKey - +key);
const kl = value[1] + (nextValue[1] - value[1]) * k;
const kq = value[2] + (nextValue[2] - value[2]) * k;
return [1, kl, kq];
}
}
return lightAttenuationTable['3250'];
}
// #endregion attenuation
// #region lesscode
export type BufferInfo = {
name: string;
buffer: WebGLBuffer;
numComponents: number;
isIndices?: boolean;
};
export function createBufferInfoFromArrays(
gl: RenderContext,
arrays: {
name: string;
numComponents: number;
data: Iterable<number>;
isIndices?: boolean;
}[]
): BufferInfo[] {
const result: BufferInfo[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) {
const buffer = gl.createBuffer();
if (!buffer) {
continue;
}
result.push({
name: arrays[i].name,
buffer: buffer,
numComponents: arrays[i].numComponents,
isIndices: arrays[i].isIndices,
});
if (arrays[i].isIndices) {
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
gl.bufferData(
gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,
new Uint32Array(arrays[i].data),
gl.STATIC_DRAW
);
} else {
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
gl.bufferData(
gl.ARRAY_BUFFER,
new Float32Array(arrays[i].data),
gl.STATIC_DRAW
);
}
}
return result;
}
export type AttributeSetters = Record<string, (bufferInfo: BufferInfo) => void>;
export function createAttributeSetter(
gl: RenderContext,
program: WebGLProgram
): AttributeSetters {
const createAttribSetter = (index: number) => {
return function (b: BufferInfo) {
if (!b.isIndices) {
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, b.buffer);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(index);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
index,
b.numComponents,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
0,
0
);
}
};
};
const attribSetter: AttributeSetters = {};
const numAttribs = gl.getProgramParameter(program, gl.ACTIVE_ATTRIBUTES);
for (let i = 0; i < numAttribs; i++) {
const attribInfo = gl.getActiveAttrib(program, i);
if (!attribInfo) {
break;
}
const index = gl.getAttribLocation(program, attribInfo.name);
attribSetter[attribInfo.name] = createAttribSetter(index);
}
return attribSetter;
}
export type UniformSetters = Record<string, (v: any) => void>;
export function createUniformSetters(
gl: RenderContext,
program: WebGLProgram
): UniformSetters {
let textUnit = 0;
const createUniformSetter = (
program: WebGLProgram,
uniformInfo: {
name: string;
type: number;
}
): ((v: any) => void) => {
const location = gl.getUniformLocation(program, uniformInfo.name);
const type = uniformInfo.type;
if (type === gl.FLOAT) {
return function (v: number) {
gl.uniform1f(location, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_VEC2) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniform2fv(location, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_VEC3) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniform3fv(location, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_VEC4) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniform4fv(location, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_MAT2) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniformMatrix2fv(location, false, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_MAT3) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniformMatrix3fv(location, false, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.FLOAT_MAT4) {
return function (v: number[]) {
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(location, false, v);
};
} else if (type === gl.SAMPLER_2D) {
const currentTexUnit = textUnit;
++textUnit;
return function (v: WebGLTexture) {
gl.uniform1i(location, currentTexUnit);
gl.activeTexture(gl.TEXTURE0 + currentTexUnit);
gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, v);
};
}
return function () {
throw new Error('cannot find corresponding type of value.');
};
};
const uniformsSetters: UniformSetters = {};
const numUniforms = gl.getProgramParameter(program, gl.ACTIVE_UNIFORMS);
for (let i = 0; i < numUniforms; i++) {
const uniformInfo = gl.getActiveUniform(program, i);
if (!uniformInfo) {
break;
}
let name = uniformInfo.name;
if (name.substr(-3) === '[0]') {
name = name.substr(0, name.length - 3);
}
uniformsSetters[uniformInfo.name] = createUniformSetter(
program,
uniformInfo
);
}
return uniformsSetters;
}
export function setAttribute(
attribSetters: AttributeSetters,
bufferInfos: BufferInfo[]
) {
for (let i = 0; i < bufferInfos.length; i++) {
const info = bufferInfos[i];
const setter = attribSetters[info.name];
setter && setter(info);
}
}
export function setUniform(
uniformSetters: UniformSetters,
uniforms: Record<string, any>
): void {
const keys = Object.keys(uniforms);
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
const key = keys[i];
const v = uniforms[key];
const setter = uniformSetters[key];
setter && setter(v);
}
}
// #endregion lesscode
export function fromViewUp(view: Vector3, up?: Vector3): Matrix4 {
up = up || new Vector3(0, 1, 0);
const xAxis = new Vector3().crossVectors(up, view);
xAxis.normalize();
const yAxis = new Vector3().crossVectors(view, xAxis);
yAxis.normalize();
// prettier-ignore
return new Matrix4(
xAxis.x, yAxis.x, view.x, 0,
xAxis.y, yAxis.y, view.y, 0,
xAxis.z, yAxis.z, view.z, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1
)
}
export function getMirrorPoint(
p: Vector3,
n: Vector3,
origin: Vector3
): Vector3 {
const op = p.clone().sub(origin);
const normalizedN = n.clone().normalize();
const d = op.dot(normalizedN);
const newP = op.sub(normalizedN.multiplyScalar(2 * d));
return newP;
}
export function getMirrorVector(p: Vector3, n: Vector3): Vector3 {
const normalizedN = n.clone().normalize();
const d = p.dot(normalizedN);
return normalizedN.multiplyScalar(2 * d).sub(p);
}
export function setReflection2(
mainCamera: Camera,
virtualCamera: Camera,
reflector: Object3D
): void {
const reflectorWorldPosition = new Vector3();
const cameraWorldPosition = new Vector3();
reflectorWorldPosition.setFromMatrixPosition(reflector.matrixWorld);
cameraWorldPosition.setFromMatrixPosition(mainCamera.matrixWorld);
const rotationMatrix = new Matrix4();
rotationMatrix.extractRotation(reflector.matrixWorld);
const normal = new Vector3();
normal.set(0, 0, 1);
normal.applyMatrix4(rotationMatrix);
const view = new Vector3();
view.subVectors(reflectorWorldPosition, cameraWorldPosition);
view.reflect(normal).negate();
view.add(reflectorWorldPosition);
rotationMatrix.extractRotation(mainCamera.matrixWorld);
const lookAtPosition = new Vector3();
lookAtPosition.set(0, 0, -1);
lookAtPosition.applyMatrix4(rotationMatrix);
lookAtPosition.add(cameraWorldPosition);
const target = new Vector3();
target.subVectors(reflectorWorldPosition, lookAtPosition);
target.reflect(normal).negate();
target.add(reflectorWorldPosition);
virtualCamera.position.copy(view);
virtualCamera.position.copy(view);
virtualCamera.up.set(0, 1, 0);
virtualCamera.up.applyMatrix4(rotationMatrix);
virtualCamera.up.reflect(normal);
virtualCamera.isCamera = true;
virtualCamera.lookAt(target);
if (
virtualCamera instanceof PerspectiveCamera &&
mainCamera instanceof PerspectiveCamera
) {
virtualCamera.far = mainCamera.far; // Used in WebGLBackground
virtualCamera.updateMatrixWorld();
virtualCamera.projectionMatrix.copy(mainCamera.projectionMatrix);
} else {
// reflectCamera.updateMatrixWorld();
}
}TranslateX
TranslateY
Rotation
Scale
总结
OK,今天我们介绍了仿射变换是怎样一回事,实际上仿射变换跟 WebGL 的关系并不大,实际上它应该属于是图形学领域的内容,但是我们不得不学习仿射变化,因为如果我们不理解仿射变换的话,我们将在 WebGL 的世界中寸步难行。
可能这一章的内容稍微有一点多并且有点难,但是我还是希望你能够仔细的阅读本文,完全理解仿射变换是非常的有必要的。
在最后我们给出的 demo 中,你可以发现某些问题,比如我们在旋转三角形的时候,你会发现三角形发生了变形!这是因为我们的画布的尺寸被归一化了,但是画布的宽高比并不等于 1:1 导致的。接下来我们将介绍投影矩阵来解决这个问题,下一章再见 👋🏻!
如果觉得本文有用,可以请作者喝杯咖啡~

