Appearance
光照(二)——点光源与聚光灯
前言
在上一篇文章光照(一)中,我们介绍了在平行光中实现的 Phong 基本光照模型。
之前介绍的平行光作为照亮整个场景的全局光源来说是非常棒的选择,但是除了平行光之外我们也需要一些分散在场景中的其他光源,想想一下在洞穴中墙壁上的火把或者是城市夜晚中的路灯,都是很典型的点光源。除了点光源之外,还有一些其他的光源类型。今天我们为大家再介绍两种常见的光照模型:“点光源”与“聚光灯”。
点光源
点光源,顾名思义,就是用一个点来表示该光源所处的位置。点光源不同于平行光在场景中任意位置的强度都相同,我们认为点光源的辐射范围是有限的。当物体不在点光源的辐射范围内时,则该物体不被该光源所影响。如果物体处于点光源的辐射范围内,我们还需要考虑点光源在其范围内的衰减情况。换句话说,我们希望离光源越近的物体被照的约亮,离光源越远的物体则偏暗一些。
衰减
随着光线传播距离的增长逐渐削减光的强度通常叫做衰减(Attenuation)。我们可以通过很多方式来表示这样的一种情况,比如使用线性方程等,不过使用线性方程来解决这一问题时会让其看起来非常的“假”。我们通常采用非线性的变化来表示光照的衰减。幸运的是已经有人帮我们解决了这个问题,我们通常采用下面这个公式来计算光源的衰减:
其中:
- 表示常数项,通常为 1
- 表示一次项,它与距离相乘,以线性的方式减少强度
- 表示二次项,它与距离的二次方相乘,让光源以二次方递减的速度减少强度。当光源与被照射物之间的距离比较小时,一次项的影响比较大,但是当距离比较大的时候,则是二次项的影响更大了。下图显示了在 13 距离内的衰减效果。
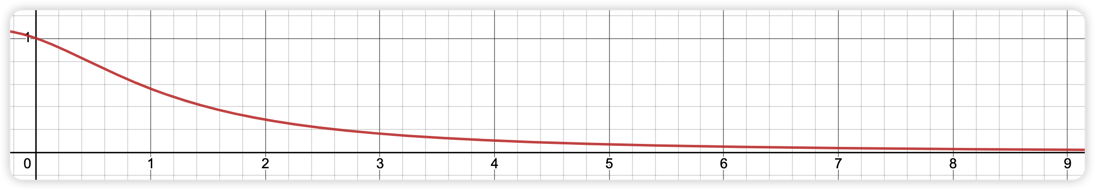
但是,对于一个某个辐射范围的点光源的这三个系数该如何确定呢?比如说:我创建了一个辐射范围为 100 的点光源,那么这个点光源所对应的 都分别是多少呢?
在 Ogre 这个开源的 3D 引擎中,提供了这样的参数参照:
| 距离 | 常数项 | 一次项 | 二次项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.8 |
| 13 | 1.0 | 0.35 | 0.44 |
| 20 | 1.0 | 0.22 | 0.20 |
| 32 | 1.0 | 0.14 | 0.07 |
| 50 | 1.0 | 0.09 | 0.032 |
| 65 | 1.0 | 0.07 | 0.017 |
| 100 | 1.0 | 0.045 | 0.0075 |
| 160 | 1.0 | 0.027 | 0.0028 |
| 200 | 1.0 | 0.022 | 0.0019 |
| 325 | 1.0 | 0.014 | 0.0007 |
| 600 | 1.0 | 0.007 | 0.0002 |
| 3250 | 1.0 | 0.0014 | 0.000007 |
点光源实现
现在我们将之前的平行光的光照改为点光源的光照。我们不需要改变顶点着色器中的内容,我们仅仅只需要改变片元着色器中的内容。
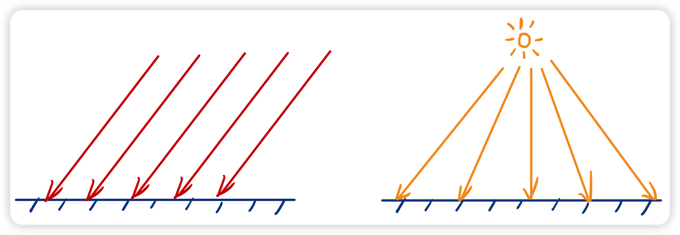
首先,对于物体表面的每个点来说,光源的方向会变得不一样,如下图所示。我们需要根据光源的位置和物体表面的位置来计算光照方向。另外,我们还需要计算光源到物体表面的距离。最后根据的值来计算衰减度。
glsl
uniform vec3 u_coefficient;
// ......
float kc = u*coefficient[0];
float kl = u_coefficient[1];
float kq = u_coefficient[2];
// ......
vec3 lightDir = normalize(u_lightDir);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(u_lightPos - v_worldPos);
float dis = distance(u_lightPos, v_worldPos);
float atten = 1.0 / (kc + kl * dis + kq _ dis _ dis);
vec3 color = ambient + (diffuse + specular) * atten;最终,点光源实现的 Phong 光照模型如下:
TranslateX
TranslateY
TranslateZ
Gloss
聚光灯
接下来我们要讨论的光源类型是聚光灯。聚光灯与点光源类似,它同样是位于某个位置的光源,但是它与点光源不同的是:聚光灯不会向空间的所有方向发射光线,聚光灯只会向空间中的特定方向发射光线。也就是说,只有特定区域的物体才会被聚光灯所照亮,你可以想象一下舞台上的照射在演员身上的追光灯或者是黑夜中的手电筒,它们都是典型的聚光灯。
我们要描述聚光灯,我们不仅仅需要聚光灯的位置,还需要聚光灯的照射方向,还需要聚光灯的“聚光半径”。这里我说“聚光半径”可能有一点歧义。其实我想表达的是被照射的物体表面与聚光灯形成的连线与聚光灯照射方向形成的夹角。如下图所示:
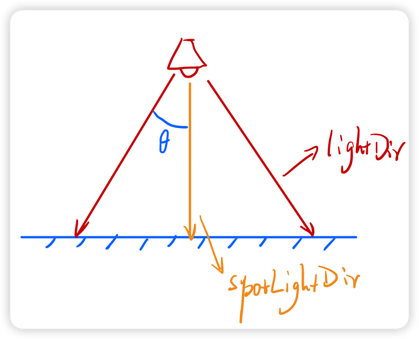
其中:
- lightDir: 表示物体表面到光源的方向
- spotLightDir: 表示聚光灯的照射方向
而表示 lightDir 与 spotLightDir 之间的夹角。如果这个夹角大于某个值,则不被照亮,这正是聚光灯的特性。所以我们需要引入一个变量 cutoff表示聚光灯能照亮物体的最大范围,一般我们用夹角的余弦值表示。因为我们在 GLSL 中可以通过点乘的方式很方便的计算余弦值。
我们可以写入下面的代码:
glsl
float LdotS = dot(-lightDir, normalize(u_spotDir));
float m = 1.0;
if (LdotS < cutoff) {
m = 0.1;
}
vec3 color = ambient + (diffuse + specular) * atten * m;结果如下:
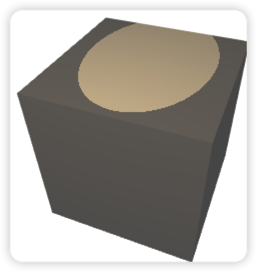
不过,我们使用 if条件判断来决定两部分的光照强度的话会产生一个硬边。我们更希望的是在有光和无光的部分能够产生一个比较平滑的过渡,所以,我们单单靠一个夹角来判断聚光灯照亮范围是不够的,我们还需要引入另一个角度 。如下图所示:
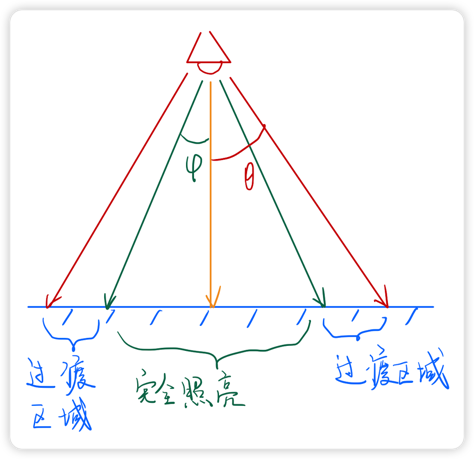
我们期望夹角小于时,物体的表面被聚光灯完全照亮,夹角处于 和 之间时,则有一段从亮到暗的过渡,夹角大于 时,则不被聚光灯照亮。在 GLSL 中正好有一个函数对应这种情况,就是 smoothstep(min, max, x)。其表示,如果 x < min 时,则返回 0,如果 x > max,则返回 1。如果处于其中,则在 0~1 之间进行插值处理。我们可以写出下面的代码:
glsl
float m = smoothstep(u_cutoff[0], u_cutoff[1], LdotS) * 0.8 + 0.2;
vec3 color = ambient + (diffuse + specular) * atten * m;上面,我们进行了 *0.8 + 0.2 的运算,是因为我们想让聚光灯外的亮度没有那么的黑,所以将 0~1 的返回值范围调整为了 0.2~1 之间。
总结
本文介绍了点光源和聚光灯这两种常见的光源形式,再加上之前我们使用的平行光,我们已经学习了三种光源了。恰当的使用光源可以给场景带来不错的氛围效果。源代码见文末。
TranslateX
TranslateY
TranslateZ
Gloss
如果觉得本文有用,可以请作者喝杯咖啡~


ts
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas4') as HTMLCanvasElement;
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl');
if (!gl) {
return null;
}
// 设置清空颜色缓冲区时的颜色
gl.clearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// 清空颜色缓冲区
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// 顶点着色器
const vertexShader = lightVert;
// 片元着色器
const fragmentShader = lightFrag;
// 初始化shader程序
const program = initWebGL(gl, vertexShader, fragmentShader);
if (!program) {
return null;
}
// 告诉WebGL使用我们刚刚初始化的这个程序
gl.useProgram(program);
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);
const width = 1;
const height = 1;
const depth = 1;
//prettier-ignore
const pointPos = [
// front-face
0, 0, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, 0, 0, height, 0, 0, 0, 0,
// back-face
0, 0, depth, width, 0, depth, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, 0, depth,
// left-face
0, 0, 0, 0, height, 0, 0, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, 0, depth, 0, 0, 0,
// right-face
width, 0, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, width, 0, depth, width, 0, 0,
// top-face
0, height, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, height, 0,
// bottom-face
0, 0, 0, width, 0, 0, width, 0, depth, width, 0, depth, 0, 0, depth, 0, 0, 0,
];
//prettier-ignore
const normals = [
// front-face
0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1,
// back-face
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// left-face
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,
// right-face
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
// top-face
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom-face
0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0,
];
for (let i = 0; i < pointPos.length; i += 3) {
pointPos[i] += -width / 2;
pointPos[i + 1] += -height / 2;
pointPos[i + 2] += -depth / 2;
}
//prettier-ignore
const colors = [
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
]
const buffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(pointPos), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
const colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(colors), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
const normalBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(normals), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
// 获取shader中a_position的地址
const a_position = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_position');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
// gl.vertexAttrib3f(a_position, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// 采用vertexAttribPointer进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_position,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_position);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
const a_color = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_color');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_color,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_color);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
const a_normal = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_normal');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_normal,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_normal);
// 我们需要往shader中传入矩阵
const uWorldLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_world');
const uViewInvLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_viewInv');
const uLightPos = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_lightPos');
const uViewPosLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_viewWorldPos');
const uGlossLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_gloss');
const uCoefficientLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_coefficient');
const uSpotDirLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_spotDir');
const uCutoffLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_cutoff');
let translateX = 0; //
let translateY = 0; //
let translateZ = 0; //
const uProj = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_proj');
const projMat = mat4.create();
mat4.perspective(projMat, 45, canvas.width / canvas.height, 1, 2000);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uProj, false, projMat);
let cameraMat = mat4.create();
const worldMat = mat4.create();
mat4.translate(worldMat, worldMat, [0, 0, 0]);
const pointLightPos = vec3.fromValues(0, 2, 1.5);
let gloss = 64;
const coEfficient = lightAttenuationLookUp(30);
const render = () => {
gl.useProgram(program);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); //
mat4.identity(cameraMat);
const cameraPos = vec3.fromValues(translateX, translateY, translateZ);
cameraMat = lookAt(
new Float32Array([translateX, translateY, translateZ]),
new Float32Array([0, 0, 0])
);
mat4.invert(cameraMat, cameraMat);
const cameraWorldPos = vec3.create();
vec3.transformMat4(cameraWorldPos, cameraPos, worldMat);
const pointLightWorldPos = vec3.create();
vec3.transformMat4(pointLightWorldPos, pointLightPos, worldMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uWorldLoc, false, worldMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uViewInvLoc, false, cameraMat);
gl.uniform3fv(uLightPos, pointLightWorldPos);
gl.uniform3fv(uViewPosLoc, cameraWorldPos);
gl.uniform3fv(uCoefficientLoc, coEfficient);
gl.uniform3fv(uSpotDirLoc, [0, -1, -1]);
gl.uniform2fv(uCutoffLoc, [
Math.cos((10 / 180) * Math.PI),
Math.cos((9 / 180) * Math.PI),
]);
gl.uniform1f(uGlossLoc, gloss);
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, pointPos.length / 3);
};
render();ts
export function lightAttenuationLookUp(dist: number): number[] {
const distKeys = Object.keys(lightAttenuationTable);
const first = +distKeys[0];
if (dist <= first) {
return lightAttenuationTable['7'];
}
for (let i = 0; i < distKeys.length - 1; i++) {
const key = distKeys[i];
const nextKey = distKeys[i + 1];
if (+key <= dist && dist < +nextKey) {
const value = lightAttenuationTable[key];
const nextValue = lightAttenuationTable[nextKey];
const k = (dist - +key) / (+nextKey - +key);
const kl = value[1] + (nextValue[1] - value[1]) * k;
const kq = value[2] + (nextValue[2] - value[2]) * k;
return [1, kl, kq];
}
}
return lightAttenuationTable['3250'];
}glsl
attribute vec4 a_position;
attribute vec3 a_color;
attribute vec3 a_normal;
uniform mat4 u_world;
uniform mat4 u_viewInv;
uniform mat4 u_proj;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
varying vec3 v_normal;
void main() {
vec4 worldPos = u_world * a_position;
vec4 worldNormal = u_world * vec4(a_normal, 1.0);
v_worldPos = worldPos.xyz / worldPos.w;
v_color = a_color;
v_normal = worldNormal.xyz / worldNormal.w;
gl_Position = u_proj * u_viewInv * worldPos;
}glsl
precision mediump float;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_normal;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
uniform vec3 u_viewWorldPos;
uniform float u_gloss;
uniform vec3 u_lightPos;
uniform vec3 u_coefficient;
uniform vec3 u_spotDir;
uniform vec2 u_cutoff;
void main() {
float kc = u_coefficient[0];
float kl = u_coefficient[1];
float kq = u_coefficient[2];
vec3 n = normalize(v_normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(u_lightPos - v_worldPos);
float dis = distance(u_lightPos, v_worldPos);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(u_viewWorldPos - v_worldPos);
vec3 r = normalize(2.0 * dot(n, lightDir) * n - lightDir);
float atten = 1.0 / (kc + kl * dis + kq * dis * dis);
float LdotN = dot(lightDir, n);
float RdotV = dot(viewDir, r);
float LdotS = dot(-lightDir, normalize(u_spotDir));
float m = smoothstep(u_cutoff[0], u_cutoff[1], LdotS) * 0.8 + 0.2;
vec3 dColor = vec3(1.0, 0.8, 0.5);
vec3 sColor = vec3(1.0, 0.8, 0.5);
vec3 ambient = vec3(0.2);
vec3 diffuse = dColor * max(0.0, LdotN);
vec3 specular = sColor * pow(max(0.0, RdotV), u_gloss);
vec3 color = ambient + (diffuse + specular) * atten * m;
color = pow(color, vec3(1.0 / 1.5));
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}