Appearance
光照(一)

前言
光照是渲染技术中非常重要的一部分内容。“渲染”简单的讲就是解决这样的一个问题:“当前屏幕上的这个像素点应该是什么颜色?”。决定该像素点的颜色过程,我们称之为“着色(Shading)”。
通过之前的学习,我们已经能够绘制出一个每个面具有不同颜色的立方体了。但是似乎我们的立方体还缺少了点什么东西。它就是“光”。
参照现实世界中,一个物体的颜色在不同的环境中往往是不一样的,比如白色的衣服在晴天的正午时最接近于白色,如果在黄色的路灯下,它看起来更加接近黄色。衣服的颜色往往取决于光以及物体对光的“反应”。
“反应”一词表示的是物体对光的吸收、反射、散射等等作用,不同的物体有着不同的表现。正如我们上面所说的:“白色的衣服”。为什么我们我们看到这件衣服是白色的,那是因为这件衣服反射了所有波长的光线。
通常来讲,我们要模拟光照环境来进行渲染通常需要考虑 3 中物理现象。
- 光源是必须的,光源是光线的生产者
- 光线和场景中的物体发生“反应”,即一些光线被吸收,另一些光线则被反射会散射。
- 一些光线进入了摄像机中,产生了图像。
光源
光源是光线发出的源头。在实时渲染中,我们通常有以下几种光源:
- 平行光,该光源没有实际的位置,只具有方向。对于空间中的任何一点来说其光线方向都是相同的。
- 点光源,把光源当成一个没有体积的点,向四方八方发射光源。
- 聚光灯,类似于舞台上的聚光灯。
光照模型
光照模型是一类数学公式,它指导我们如何计算光照。光照模型有很多种,早在 1975 年,Bui Tuong Phong 就提出了一套光照模型,也是我们今天着重介绍的光照模型——Phong 光照模型。
它的基本方法是:将光照分为 4 个部分,每个部分使用一种方法来计算它,最终将 4 个部分相加得到最终的结果。这 4 个部分是:
- 自发光(emissive),表示该物体自身是否会发出光线
- 环境光(ambient),表示其他所有的间接光照
- 漫反射(diffuse),表示光线从光源直接照射到物体表面是,该表面会向每个方向散射多少能量。
- 高光反射(specular),表示光源直接照射到物体表面时,该表面会完全镜面反射多少能量。
Phong 光照模型最主要关心的则是漫反射和高光反射两个部分(直接光照)。
环境光
虽然 Phong 光照模型的重点在于直接光照,但是在真实的世界中,物体也可以被间接光照所照亮
TIP
间接光照的意思是光线通常会在多个物体之间来回的反射,最终进入摄像机内。在生活中我们通常会注意到这样的一个现象,在红地毯上放置一件浅色物品,那么这个物品接近地毯的部分看起来也会略微发红。
但是,间接光照的计算十分的复杂。它是现阶段图形学中的难题之一。所以为了简单期间,在 Phong 模型中,我们通常使用一个常亮来表示间接光照。
自发光
光线也可以不经过任何反射直接进入相机。它的计算也很简单,也是使用一个常亮来表示一个自发光物体的光照。
漫反射
漫反射是用于哪些被物体表面随机散射到各个方向的能量进行建模的。在漫反射中,由于反射的方向是随机的,我们可以简单的认为观察者的位置并不重要。但是,光线入射的角度很重要。
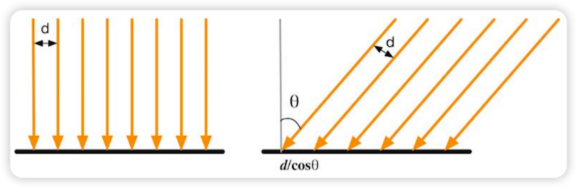
如上图所示,入射的光线角度不同时,单位面积所接受的能量是不一样的。入射光线的角度越大(约水平),则接受的能量越小。在 Phong 光照模型中,我们表示为:
其中 是表面发现,是指光源的单位方向,是材质的漫反射颜色,是光源的颜色。我们在光源单位向量和法线做点乘后,我们增加了一个 max运算符,这是因为我们需要防止法线和光源的方向的点乘的结果为负值。
TIP
通常这种情况发生在物体的背面与光源单位向量相乘时
高光反射
Phong 模型中的高光反射是一种经验模型,它并完全符合真实世界中的高光反射现象。想象一下在生活中利用镜子反射光线的例子,我们通常可以利用镜子反射光线在墙面上形成一个光斑。当这个光斑照在人眼上时,就会感到非常耀眼的光亮。这是因为你通过镜子直接看到了光源。
所以,镜面反射不仅仅与光线的入射角度有关,还与观察者是否看到了反射后的光线有关。
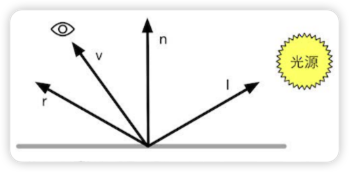
反射后的光线方向可以用下面的公式进行计算:
Phong 模型中计算高光反射的部分如下:
其中,表示材质的光泽度,这个值越大,高光区域的光斑就越小,反之光斑就越大。同样的,这里也同样需要max计算防止点乘的结果为负数。
实现
我们沿用三维相机中的代码,略微进行修改。首先我们梳理一下我们引入了哪些东西:
- 物体的法线方向
a_normal - 光源方向
u_lightDir - 相机的世界坐标
u_viewWorld, - 物体的光泽度:
u_gloss
除此之外,我们还需要在顶点着色器中计算一些东西:
- 世界空间下的法线方向:
v_normal - 世界空间下的坐标:
v_worldPos,用于计算相机与观察点之间的方向
所以,我们额外引入了 1 个 attribute变量,3 个uniform变量,2 个在顶点坐标系中计算的 varying变量。
引入新的 Attribute 变量
与之前新增颜色值类似。
ts
const normals = [
// front-face
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// back-face
0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1,
// left-face
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,
// right-face
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
// top-face
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom-face
0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0,
];
const normalBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(normals), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
const a_normal = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_normal');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_normal,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_normal);新增 Uniform 变量
ts
const uLightDirLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_lightDir');
const uViewPosLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_viewWorldPos');
const uGlossLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_gloss');修改着色器
着色器是本文的重点,我们需要按照之前介绍的理论实现这个 Phong 光照模型。
顶点着色器
首先是顶点着色器,我们在顶点着色器中计算了世界空间中的法线向量和世界空间中的顶点位置,并让他们进行光栅化进而传递到片元着色器
glsl
attribute vec4 a_position;
attribute vec3 a_color;
attribute vec3 a_normal;
uniform mat4 u_world;
uniform mat4 u_viewInv;
uniform mat4 u_proj;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
varying vec3 v_normal;
void main() {
vec4 worldPos = u_world * a_position;
vec4 worldNormal = u_world * vec4(a_normal, 1.0);
v_worldPos = worldPos.xyz / worldPos.w;
v_normal = worldNormal.xyz / worldNormal.w;
v_color = a_color;
gl_Position = u_proj * u_viewInv * worldPos;
}片元着色器
接下来是片元着色器
glsl
precision mediump float;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_normal;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
uniform vec3 u_lightDir;
uniform vec3 u_viewWorldPos;
uniform float u_gloss;
void main() {
vec3 n = normalize(v_normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(u_lightDir);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(u_viewWorldPos - v_worldPos);
vec3 r = 2.0 * dot(n, lightDir) * n - lightDir;
float LdotN = dot(lightDir, n);
float RdotV = dot(viewDir, r);
vec3 dColor = vec3(0.5);
vec3 sColor = vec3(1.0);
vec3 ambient = vec3(0.2);
vec3 diffuse = dColor * max(0.0, LdotN);
vec3 specular = sColor * pow(max(0.0, RdotV), u_gloss);
vec3 color = ambient + diffuse + specular;
color = pow(color, vec3(1.0 / 1.5));
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}上面的代码还是很容易懂的,就是对上面提到的理论的翻译,此处就不再过多的赘述了。完整代码见文末。
TranslateX
TranslateY
TranslateZ
Gloss
如果觉得本文有用,可以请作者喝杯咖啡~


ts
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas3') as HTMLCanvasElement;
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl');
if (!gl) {
return null;
}
// 设置清空颜色缓冲区时的颜色
gl.clearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
// 清空颜色缓冲区
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// 顶点着色器
const vertexShader = lightVert;
// 片元着色器
const fragmentShader = lightFrag;
// 初始化shader程序
const program = initWebGL(gl, vertexShader, fragmentShader);
if (!program) {
return null;
}
// 告诉WebGL使用我们刚刚初始化的这个程序
gl.useProgram(program);
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);
const width = 50;
const height = 50;
const depth = 50;
//prettier-ignore
const pointPos = [
// front-face
0, 0, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, 0, 0, height, 0, 0, 0, 0,
// back-face
0, 0, depth, width, 0, depth, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, 0, depth,
// left-face
0, 0, 0, 0, height, 0, 0, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, 0, depth, 0, 0, 0,
// right-face
width, 0, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, width, 0, depth, width, 0, 0,
// top-face
0, height, 0, width, height, 0, width, height, depth, width, height, depth, 0, height, depth, 0, height, 0,
// bottom-face
0, 0, 0, width, 0, 0, width, 0, depth, width, 0, depth, 0, 0, depth, 0, 0, 0,
];
//prettier-ignore
const normals = [
// front-face
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
// back-face
0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1,
// left-face
-1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0,
// right-face
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
// top-face
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
// bottom-face
0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1, 0,
];
for (let i = 0; i < pointPos.length; i += 3) {
pointPos[i] += -width / 2;
pointPos[i + 1] += -height / 2;
pointPos[i + 2] += -depth / 2;
}
//prettier-ignore
const colors = [
1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0,
1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1,
0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1, 0, 0.5, 1,
0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,
0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
]
const buffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(pointPos), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
const colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(colors), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
const normalBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(normals), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer);
// 获取shader中a_position的地址
const a_position = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_position');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
// gl.vertexAttrib3f(a_position, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// 采用vertexAttribPointer进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_position,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_position);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer);
const a_color = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_color');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_color,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_color);
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, normalBuffer);
const a_normal = gl.getAttribLocation(program, 'a_normal');
// 我们不再采用这种方式进行传值
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
a_normal,
3,
gl.FLOAT,
false,
Float32Array.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT * 3,
0
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(a_normal);
// 我们需要往shader中传入矩阵
const uWorldLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_world');
const uViewInvLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_viewInv');
const uLightDirLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_lightDir');
const uViewPosLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_viewWorldPos');
const uGlossLoc = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_gloss');
let translateX = 0; //
let translateY = 0; //
let translateZ = 0; //
const uProj = gl.getUniformLocation(program, 'u_proj');
const projMat = mat4.create();
mat4.perspective(projMat, 45, canvas.width / canvas.height, 1, 2000);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uProj, false, projMat);
let cameraMat = mat4.create();
const worldMat = mat4.create();
mat4.translate(worldMat, worldMat, [0, 0, 0]);
const lightDir = [0, 1, -1];
let gloss = 64;
const render = () => {
gl.useProgram(program);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); //
mat4.identity(cameraMat);
const cameraPos = vec3.fromValues(translateX, translateY, translateZ);
cameraMat = lookAt(
new Float32Array([translateX, translateY, translateZ]),
new Float32Array([0, 0, 0])
);
mat4.invert(cameraMat, cameraMat);
const cameraWorldPos = vec3.create();
vec3.transformMat4(cameraWorldPos, cameraPos, worldMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uWorldLoc, false, worldMat);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(uViewInvLoc, false, cameraMat);
gl.uniform3fv(uLightDirLoc, lightDir);
gl.uniform3fv(uViewPosLoc, cameraWorldPos);
gl.uniform1f(uGlossLoc, gloss);
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, pointPos.length / 3);
};
render();ts
export function lookAt(cameraPos: vec3, targetPos: vec3): mat4 {
const z = vec3.create();
const y = vec3.fromValues(0, 1, 0);
const x = vec3.create();
vec3.sub(z, cameraPos, targetPos);
vec3.normalize(z, z);
vec3.cross(x, y, z);
vec3.normalize(x, x);
vec3.cross(y, z, x);
vec3.normalize(y, y);
// prettier-ignore
return mat4.fromValues(
x[0], x[1], x[2], 0,
y[0], y[1], y[2], 0,
z[0], z[1], z[2], 0,
cameraPos[0], cameraPos[1], cameraPos[2], 1
);
}glsl
attribute vec4 a_position;
attribute vec3 a_color;
attribute vec3 a_normal;
uniform mat4 u_world;
uniform mat4 u_viewInv;
uniform mat4 u_proj;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
varying vec3 v_normal;
void main() {
vec4 worldPos = u_world * a_position;
vec4 worldNormal = u_world * vec4(a_normal, 1.0);
v_worldPos = worldPos.xyz / worldPos.w;
v_color = a_color;
v_normal = worldNormal.xyz / worldNormal.w;
gl_Position = u_proj * u_viewInv * worldPos;
}glsl
precision mediump float;
varying vec3 v_color;
varying vec3 v_normal;
varying vec3 v_worldPos;
uniform vec3 u_lightDir;
uniform vec3 u_viewWorldPos;
uniform float u_gloss;
uniform vec3 u_diffuse;
uniform vec3 u_specular;
void main() {
vec3 n = normalize(v_normal);
vec3 lightDir = -normalize(u_lightDir);
vec3 viewDir = normalize(u_viewWorldPos - v_worldPos);
vec3 r = 2.0 * dot(n, lightDir) * n - lightDir;
float LdotN = dot(lightDir, n);
float RdotV = dot(viewDir, r);
vec3 dColor = u_diffuse;
vec3 sColor = u_specular;
vec3 ambient = vec3(0.2);
vec3 diffuse = dColor * max(0.0, LdotN);
vec3 specular = sColor * pow(max(0.0, RdotV), u_gloss);
vec3 color = ambient + diffuse + specular;
color = pow(color, vec3(1.0 / 1.5));
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}